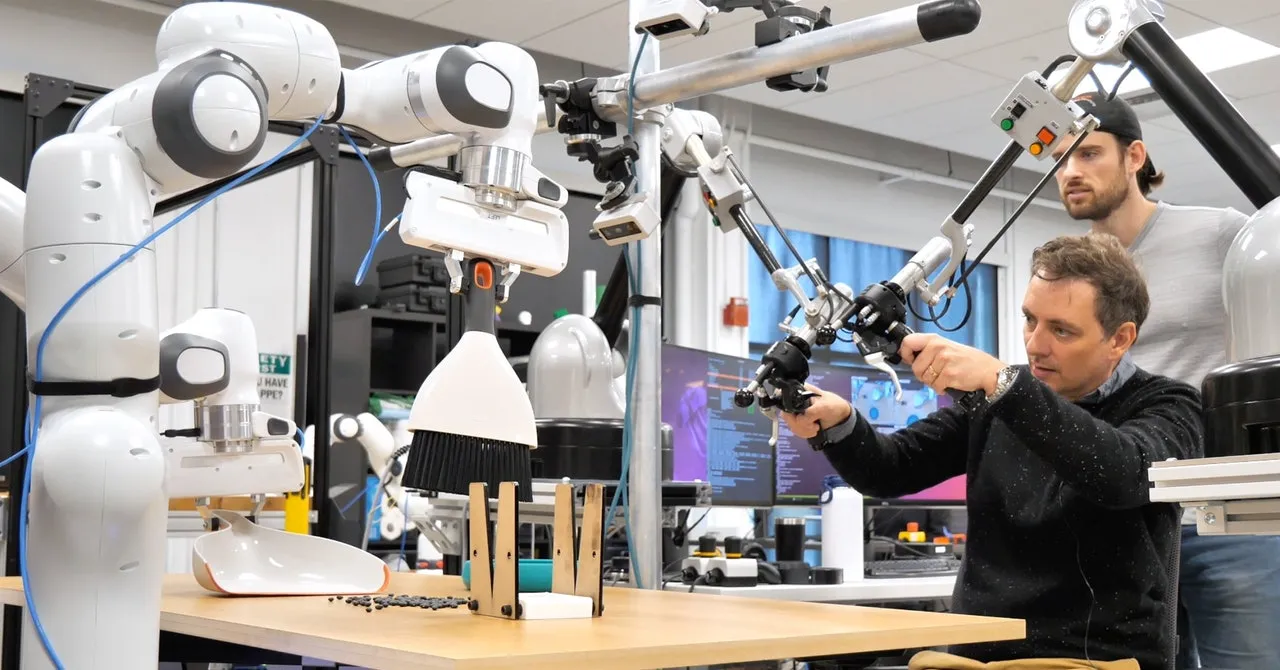
MIT’s Breakthrough: New Model for Training Robots Unveiled
In a significant leap forward for robotics, researchers at MIT have unveiled a new model for training robots that takes inspiration from the massive data sets used to train large language models (LLMs). This pioneering method presented by MIT during the current week is going to transform how robots learn and transform to new activities.
The new model for training robots departs from the traditional method of using focused data to teach robots specific skills. Instead, it adopts what can be considered a more holistic approach – imitating the vast reservoirs of knowledge used when training LLMs.
By leveraging larger and more diverse data sets, this new model for training robots aims to overcome the limitations of imitation learning, where robots struggle to adapt when faced with minor challenges such as changes in lighting, setting, or obstacles.
A Paradigm Shift in Robot Training
According to the lead author of the research paper Lirui Wang, the language domain is quite different from robotics. Even more, Wang says that in the language domain, the data are all just sentences. Thus, as for the situation in robotics given all this heterogeneity of the data we need a different architecture if we want to pretrain in a similar way.
To address this challenge, the MIT team introduced a new model for training robots called Heterogeneous Pretrained Transformers (HPT). The specific architecture allows to combine information from different sensors and environments of the system. According to the researchers, through the use of a transformer to aggregate data into the training models used, the bigger the size the transformer, the bigger the output achieved.
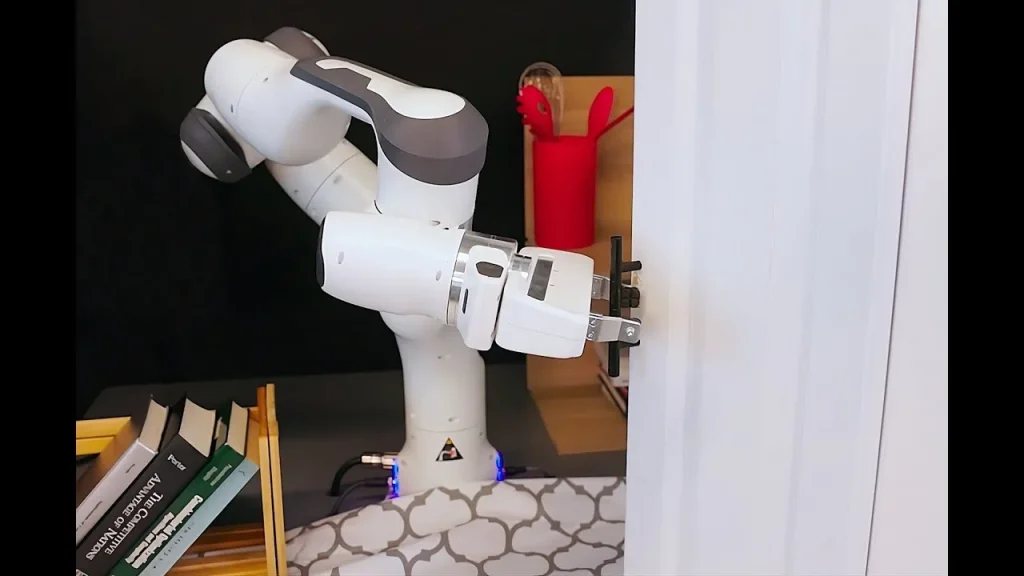

Simplifying Robot Deployment
One of the key advantages of this new model for training robots is its user-friendly approach. Again, the users only have to input the robot design and configuration and the specific task under consideration. It then becomes the responsibility of the created system to sort it out on its own without much additional training.
David Held, an associate professor at CMU, expresses the team’s long-term vision: ‘Our dream is for there to be a base robot brain that you could network download, into your robot and then didn’t have to train it at all.’ As we are now only in stage 1, we are going to have to continue to apply more pressure and see if scale drives the discovery of richer robotic policies like scale discovered in large language models.
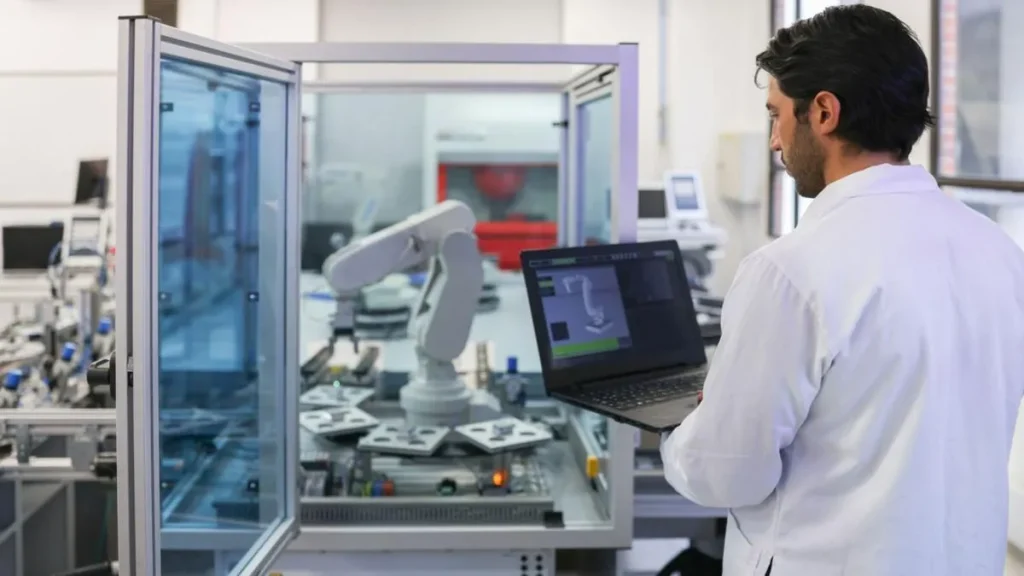

Industry Support and Collaboration
The research behind this new model for training robots has garnered support from notable industry players. Partially, Toyota Research Institute (TRI) has supported the project proving their interest in robot learning. In fact, TRI demonstrated a technique of over night training of robots at TechCrunch Disrupt last year.
Even more recently, TRI established an unprecedented collaboration with Boston Dynamics, where they combined its robot learning research with hardware leading-edge. This collaboration underscores the industry’s recognition of the potential of this new model for training robots and its implications for the future of robotics.
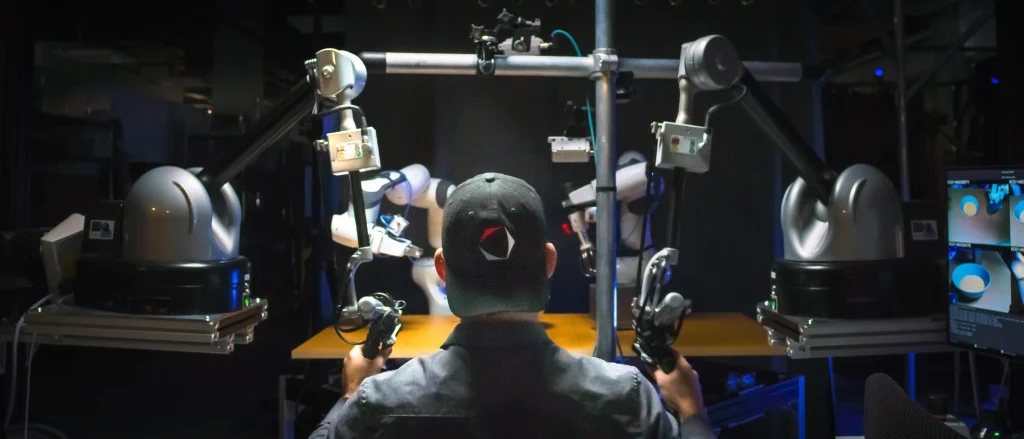

The Future of Robotics
As the field of robotics continues to evolve, the introduction of this new model for training robots marks a significant milestone. Using Big Data as inspiration from LLMs, researchers are now laying the groundwork for much more flexible, general-purpose, and intuitive robotic systems.
While there is still work to be done, the new model for training robots developed by MIT researchers holds immense promise. When research is going on and connections between academia and industry are improving the development of robot learning will continue to evolve as robots find there way into so many aspects of our lives.
The new model for training robots unveiled by MIT this week represents a bold step forward in the quest to create intelligent, adaptable robotic systems. As this approach can help to reduce the cost of robots’ deployment and let robots learn from a large number of situations, this future works has a great potential to become a breakthrough in robotics and influence the development of human-robots interaction.